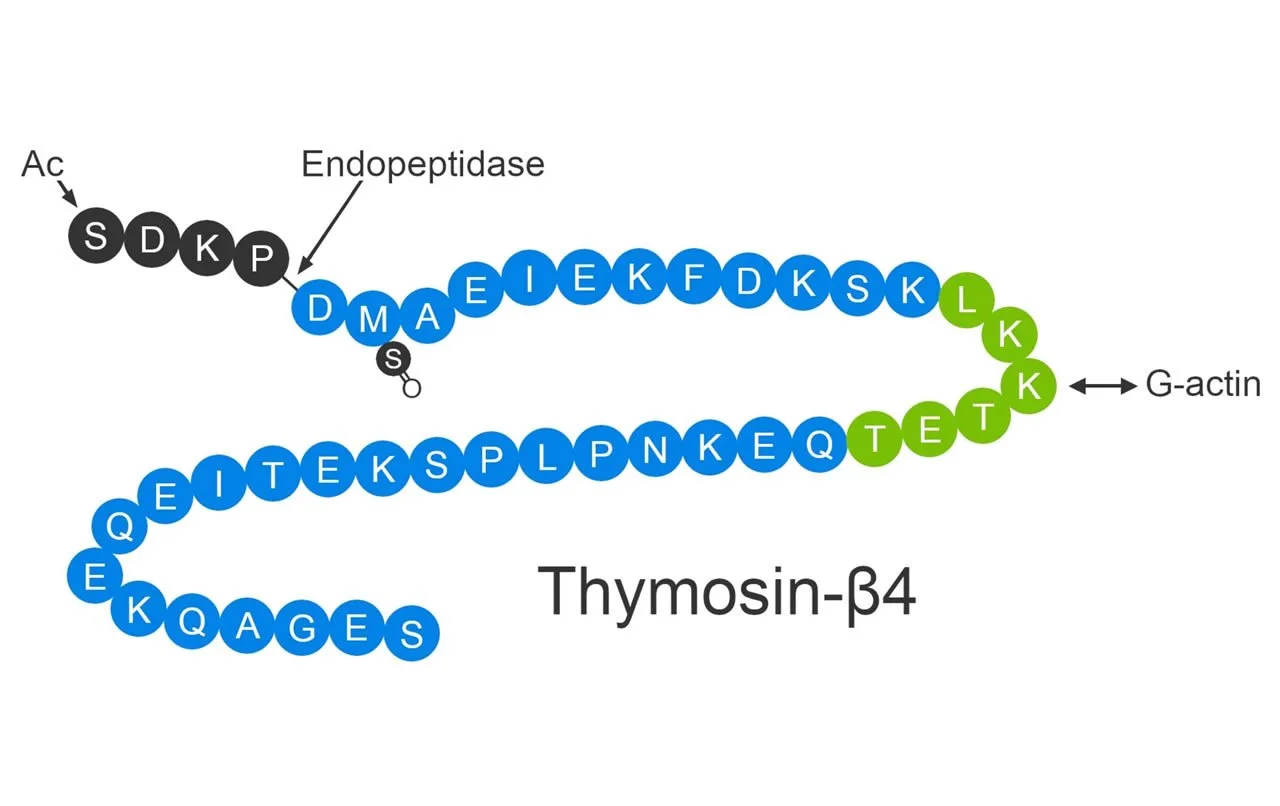
Initially identified as a protein isolate from the thymus gland, Thymosin Beta 4 belongs to the Thymosins family, characterized by acidic and lightweight molecules contributing to cell production. By modulating the polymerization of actin proteins, TB-500 may potentially impact cell differentiation and movement. It may either encourage or inhibit the formation of filaments by gathering actin monomers, affecting the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into diverse cell types like bone cells or neurons. Researchers suggest that Thymosin Beta 4 might influence the formation of new blood vessels and cell migration by manipulating actin, highlighted a potential in wound healing.
The hypothesized impacts of Thymosin Beta 4 range from tissue repair, scar prevention, inhibition of cell death, microbial growth, and inflammation. Studies on externally derived TB-500 indicate accelerated healing of injured cardiac, corneal, and dermal tissues, emphasizing its wound healing potential.
Thymosin Beta 4 has been suggested to host potential anti-inflammatory characteristics, impacting nitric oxide and prostaglandin EP4 release in cell models exposed to reactive oxygen species. TB-500 molecules are considered to be osteoclastogenic, they may play a role in bone production and enhance the stimulus-response of interleukins and pro-inflammatory cytokines in periodontium cells.
Research suggests Thymosin Beta 4 inhibits the activation of NF-κB in murine macrophages and influences the release of the anti-inflammatory peptide fragment acSDKP7. The complex mechanism governing the splitting of acSDKP7 from TB-500 involves specific peptidases, including hydrolysis by meprin – alpha. Thymosin Beta 4 exhibits potential in research studying fibrotic scarring in various organs, potentially reducing inflammation in rodents with pulmonary fibrosis.
Disclaimer: The products mentioned are not intended for human or animal consumption. Research chemicals are intended solely for laboratory experimentation and/or in-vitro testing. Bodily introduction of any sort is strictly prohibited by law. All purchases are limited to licensed researchers and/or qualified professionals. All information shared in this article is for educational purposes only.