PTD-DBM Peptide Discovery
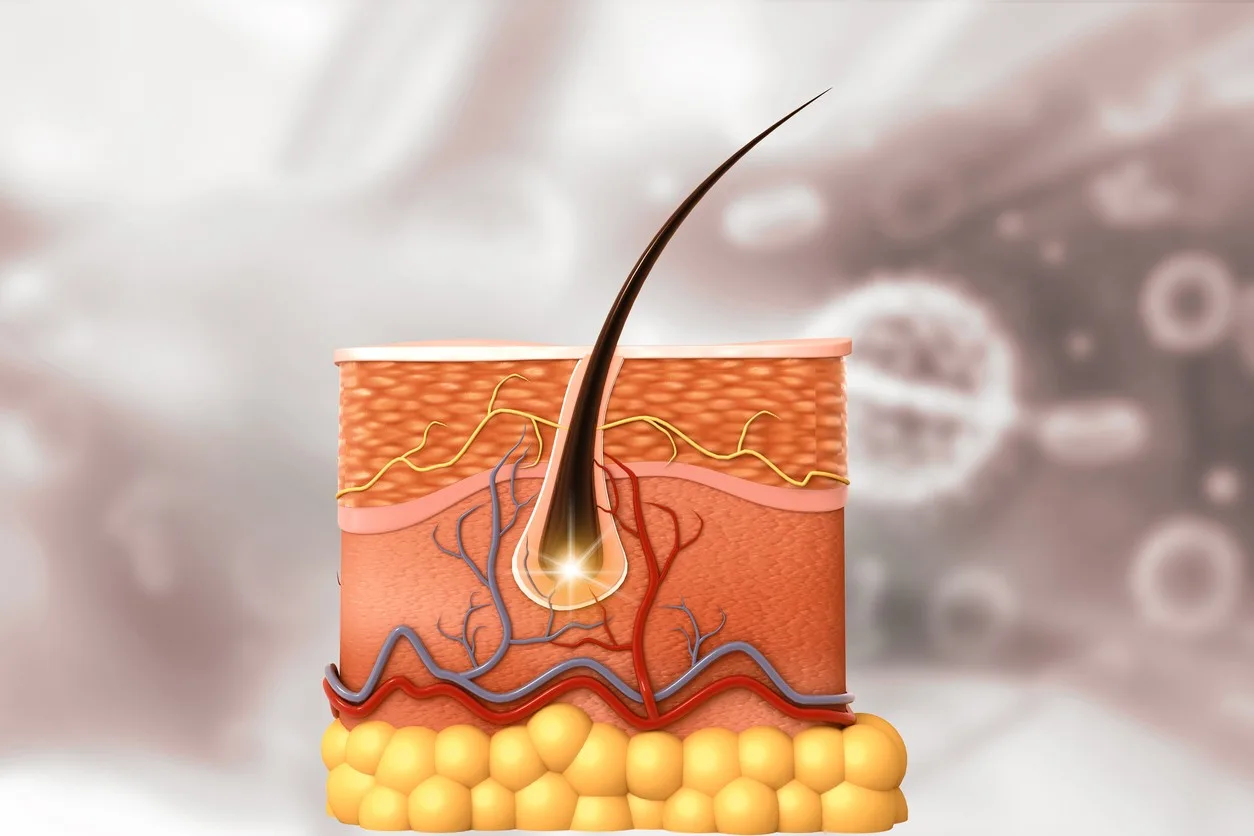
In South Korea, researchers conducted studies on a condition referred to as androgenetic alopecia. Research into this condition reportedly prompted Professor Choi Kang-yeol of Yonsei University and a team of researchers to explore a protein associated with follicle loss in androgenetic alopecia, namely CXXC5. The protein’s identification led to the discovery of the PTD-DBM peptide, which researchers suggest might interact with this protein to potentially alter the mechanism of follicle loss in the disease. It is also speculated to indirectly promote hair follicle growth in lab animals exposed to the peptide.
Mechanism Of Action
PTD-DBM peptide purportedly interferes with an endogenous protein, CXXC5, believed to be involved in the mechanism of hair loss. CXXC-type zinc finger protein 5 (CXXC5) is described as a negative regulator of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, a key pathway in wound healing and hair regeneration. Allegedly, the protein CXXC5 binds to the Dishevelled protein, impeding the growth of hair follicles and leading to hair loss. This is the point at which research into the PTD-DBM peptide may become relevant, as it is suggested to activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by interfering with the binding of CXXC5 with the Dishevelled (Dvl) protein. The claim is that PTD-DBM may promote the growth of new hair follicles and potentially inhibit the loss of existing follicles. Moreover, there are speculative assertions about its ability to induce wound repair through wound-induced hair neogenesis (WIHN).
PTD-DBM Peptide In Wound-Healing
The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is considered common to cutaneous wound healing, dermal fibrosis, and follicle regrowth. Researchers suggest that CXXC-type zinc finger protein 5 (CXXC5) may serve as a negative feedback regulator of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by interacting with the Dishevelled (Dvl) protein. The speculation researchers have made is that the PTD-DBM peptide may act as a common link between the protein CXXC5 and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Experiments on laboratory animals imply that inhibiting the CXXC5 protein might lead to accelerated cutaneous wound healing and enhanced keratin 14 and collagen synthesis. The assertion is that the PTD-DBM peptide links with the protein CXXC5, interfering with the regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and bringing about the wound-healing potential of the peptide.
Disclaimer: The products mentioned are not intended for human or animal consumption. Research chemicals are intended solely for laboratory experimentation and/or in-vitro testing. Bodily introduction of any sort is strictly prohibited by law. All purchases are limited to licensed researchers and/or qualified professionals. All information shared in this article is for educational purposes only.