Selank Peptide Overview
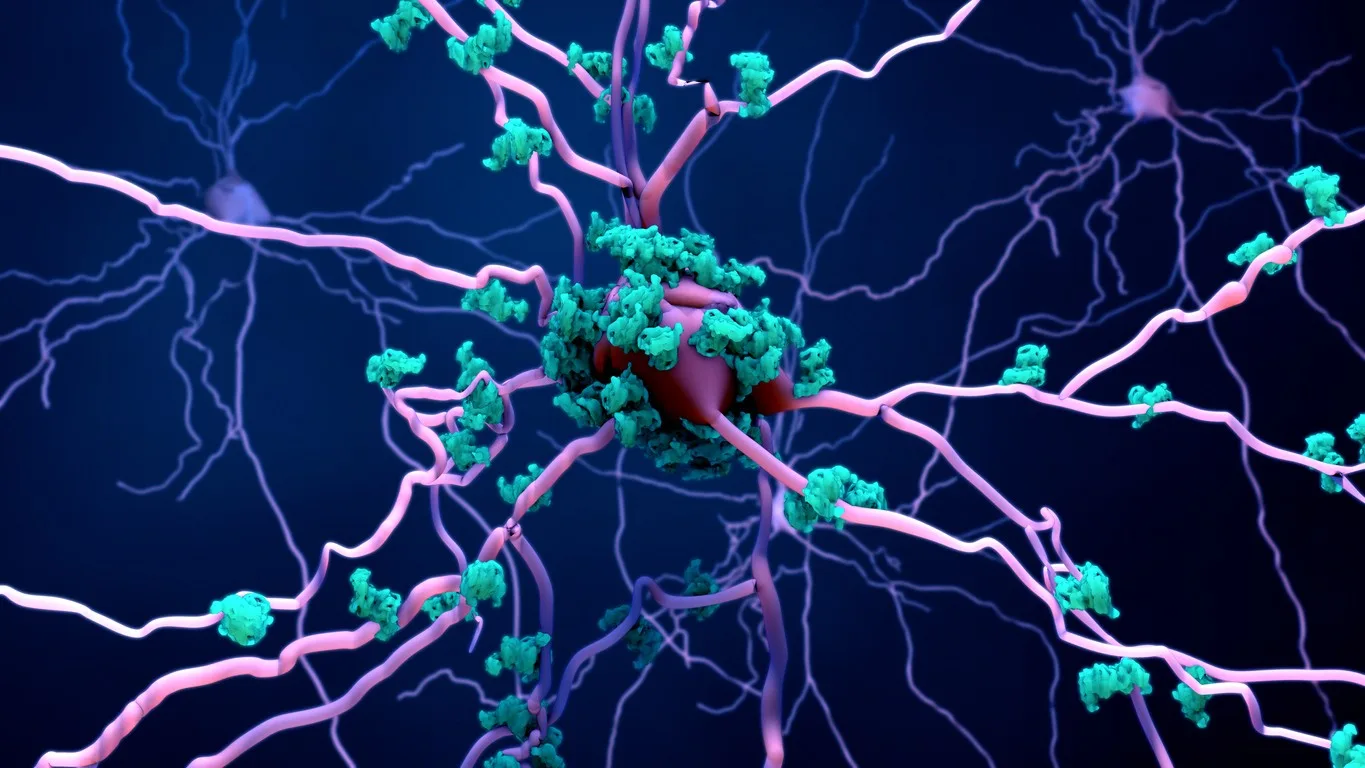
Research suggests that Selank may exhibit certain neuroprotective characteristics. Selank peptide may support mood and potentially decrease stress hormone secretion.
According to research, 84 genes have been linked to GABA signaling.[2] Selank peptide potentially regulates 7 genes, while 45 genes may induce change in expression. The net result suggests that 52 genes tied to GABA signaling may be impacted by Selank to a certain degree, suggesting that Selank may directly modulate gene expression in nerve cells and impact changes by influencing the affinity of the GABA receptor for GABA.
The impact of Selank on enkephalin degradation may potentially regulate effects on GABA receptors. According to scientific data, research models exhibit increased enkephalinase activity in the blood after stress hormone secretion, resulting in short half-lived enkephalins.
Selank peptide potentially resets the enzymatic pathway to protect the natural anxiolytic peptides by inhibiting enkephalin degradation. The research proposes that part of the Selank action may be from a preventive impact on enkephalin degradation.
Selank Peptide and Memory
Scientists believe Selank peptide may enhance certain cognitive processes.[3] Training mice with rewards, such as food, in combination with Selank, may potentially boost memory trace stability and storage. Selank’s impact in these mice models, despite anxiety levels, indicates that the peptide goes a long way to lower stress-related memory impairment.
Selank peptide may also potentially alter memory by regulating gene expression in the hippocampus. Research suggests changes in mRNA levels of 36 varying genes. Most genes encode proteins relating to the plasma membrane, regulating ion-dependent processes in memory and learning.
According to studies, Selank may potentially salvage learning and memory recall. Exposing mice samples to a neurotoxin and Selank suggested a restoration of cognitive processes. This potential correlates with an artificial inhibition of the catecholamine system in the brain via Selank. Scientists believe that Selank peptide may offer cognitive support following traumatic brain injury.
Selank Peptide and Pain Perception
Selank peptide may potentially inhibit enzymes in the blood that induce enkephalin synthesis, reducing natural enkephalin degradation. Enkephalins are peptides that bind to opioid receptors, reducing the severity of pain. They also regulate stress response and are at abnormally high levels in the adrenal glands and brain. Therefore, Selank peptide may possibly modulate stress response and its impacts on learning, concentration, and memory by lowering enkephalin levels in the brain.
Selank and the Immune System following Anxiety
Selank peptide may potentially suppress genes that control inflammatory cytokine inflammation, IL-6, in research models of depression.[4] Selank’s research in mice models suggests that the peptide may control the expression of 34 genes that influence the inflammatory process. These genes may impact cytokines, chemokines, and both receptors. Specifically, Selank peptide modulates Bcl6 expression, a gene that controls immune system development.
In addition, Selank peptide and Selank fragments may temporarily influence gene expression for Xcr1, C3, CAsp1, and II2rf in the mouse spleen. Selank may affect the immune system balance and inflammation by impacting these genes.
Disclaimer: The products mentioned are not intended for human or animal consumption. Research chemicals are intended solely for laboratory experimentation and/or in-vitro testing. Bodily introduction of any sort is strictly prohibited by law. All purchases are limited to licensed researchers and/or qualified professionals. All information shared in this article is for educational purposes only.
References
- Medvedev VE, Tereshchenko ON, Israelian AIu, Chobanu IK, Kost NV, Sokolov OIu, Miasoedov NF. [A comparison of the anxiolytic effect and tolerability of selank and phenazepam in the treatment of anxiety disorders]. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2014;114(7):17-22. Russian. PMID: 25176261.
- Volkova A, Shadrina M, Kolomin T, Andreeva L, Limborska S, Myasoedov N, Slominsky P. Selank peptide Administration Affects the Expression of Some Genes Involved in GABAergic Neurotransmission. Front Pharmacol. 2016 Feb 18;7:31. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00031. PMID: 26924987; PMCID: PMC4757669.
- Semenova TP, Kozlovskaya MM, Zakharova NM, Kozlovskii II, Zuikov AV. Effect of selank on cognitive processes after damage inflicted to the cerebral catecholamine system during early ontogeny. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2007 Nov;144(5):689-91. doi: 10.1007/s10517-007-0406-2. PMID: 18683497.
- Uchakina ON, Uchakin PN, Miasoedov NF, Andreeva LA, Shcherbenko VE, Mezentseva MV, Gabaeva MV, Sokolov OIu, Zozulia AA, Ershov FI. [Immunomodulatory effects of selank in patients with anxiety-asthenic disorders]. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2008;108(5):71-5. Russian. PMID: 18577961.