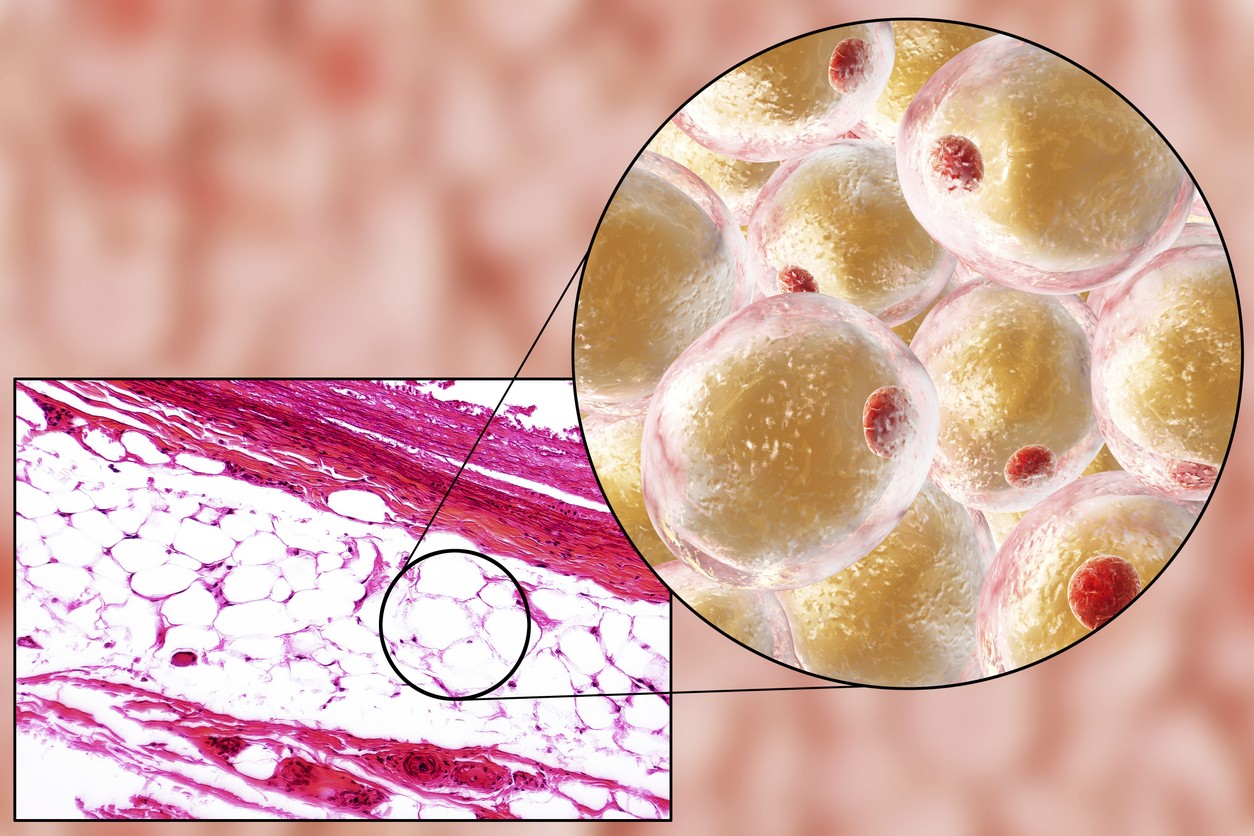
Fragment 176-191 exhibits unique potential to stimulate the metabolism of adipose tissue. A similar molecule, AOD 9604 modifies the peptide Fragment 176-191 of the growth hormone hGH by adding a tyrosine residue to the N-terminus. Research findings suggest AOD 9604 may potentially prove more effective in triggering the dissolution of fat cells, than AOD 9401, which preceded it. It has been suggested to follow the same mechanistic pathway for a fat breakdown as hGH. It may also inhibit the conversion of food fat proteins.
Studies explored the impact of exposure to Fragment 176-191 in mice, and they posited that the peptide may have reduced the fat burden in the exposed animals through induction of weight loss. The precise reason for this finding is not yet completely understood. However, scientists opine that the binding of the peptide to beta(3)-adrenergic receptors on the surface of white adipose tissues may trigger the fat metabolism process.
These receptors are strongly associated with fat metabolism. The peptide binding to the cognate receptors may induce downstream signaling for mobilizing the stored fat cells to a usable state by increasing the rate of metabolism. Interestingly, studies in mice that genetically lack β-3-adrenergic receptors also observed fat loss, possibly through apoptosis of the white adipose tissues.
Fragment 176-191 and Cardiac Disease
The burden of fat, if relieved, may lead to a cascade of beneficial downstream actions, most prominently on the cardiovascular system and the heart. Fragment 176-191 may potentially impact cardiac function by mobilizing fat and reducing obesity. One considered pathology of cardiac disease is obesity, and these pathways appear to be independent of β-3-adrenergic receptors and may contribute to improving general metabolism and cardiac function.
Joint Pain and Function
Studies involving Fragment 176-191 have suggested that it may directly impact the proliferation of cells which comprise cartilage. Directly introducing the peptide into arthritic joints in rats was reported to reduce pain perception and appeared to decrease movement disability. Scientific examination and microscopic cartilage structure analysis in the affected joints have suggested positive impact upon exposure to Fragment 176-191 in rat models of osteoarthritis.
Disclaimer: The products mentioned are not intended for human or animal consumption. Research chemicals are intended solely for laboratory experimentation and/or in-vitro testing. Bodily introduction of any sort is strictly prohibited by law. All purchases are limited to licensed researchers and/or qualified professionals. All information shared in this article is for educational purposes only.