Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 (1mg)
$145.00
IGF-1 LR3 peptides are Synthesized and Lyophilized in the USA.
Discount per Quantity
| Quantity | 5 - 9 | 10 + |
|---|---|---|
| Discount | 5% | 10% |
| Price | $137.75 | $130.50 |
FREE - USPS priority shipping
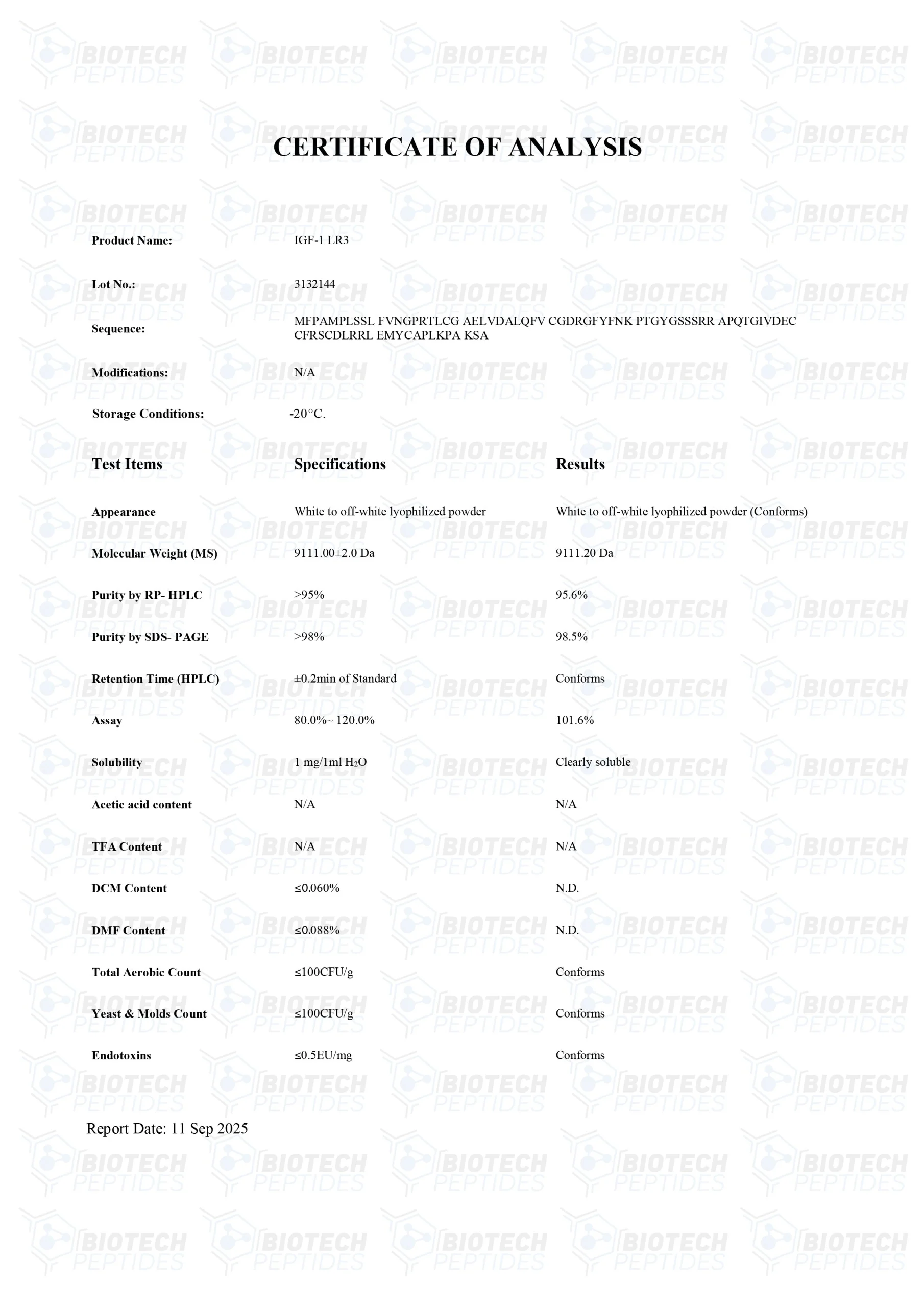
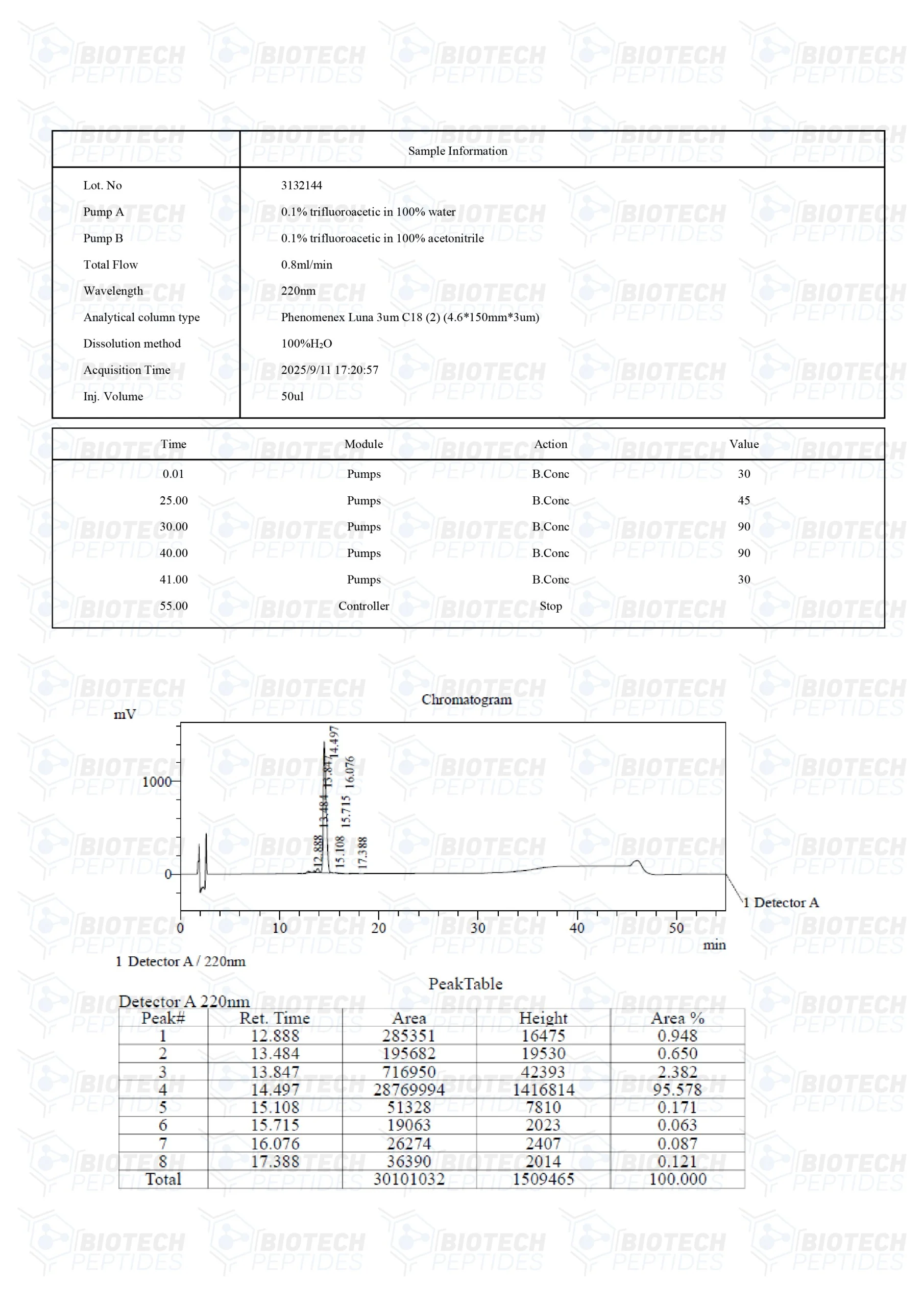
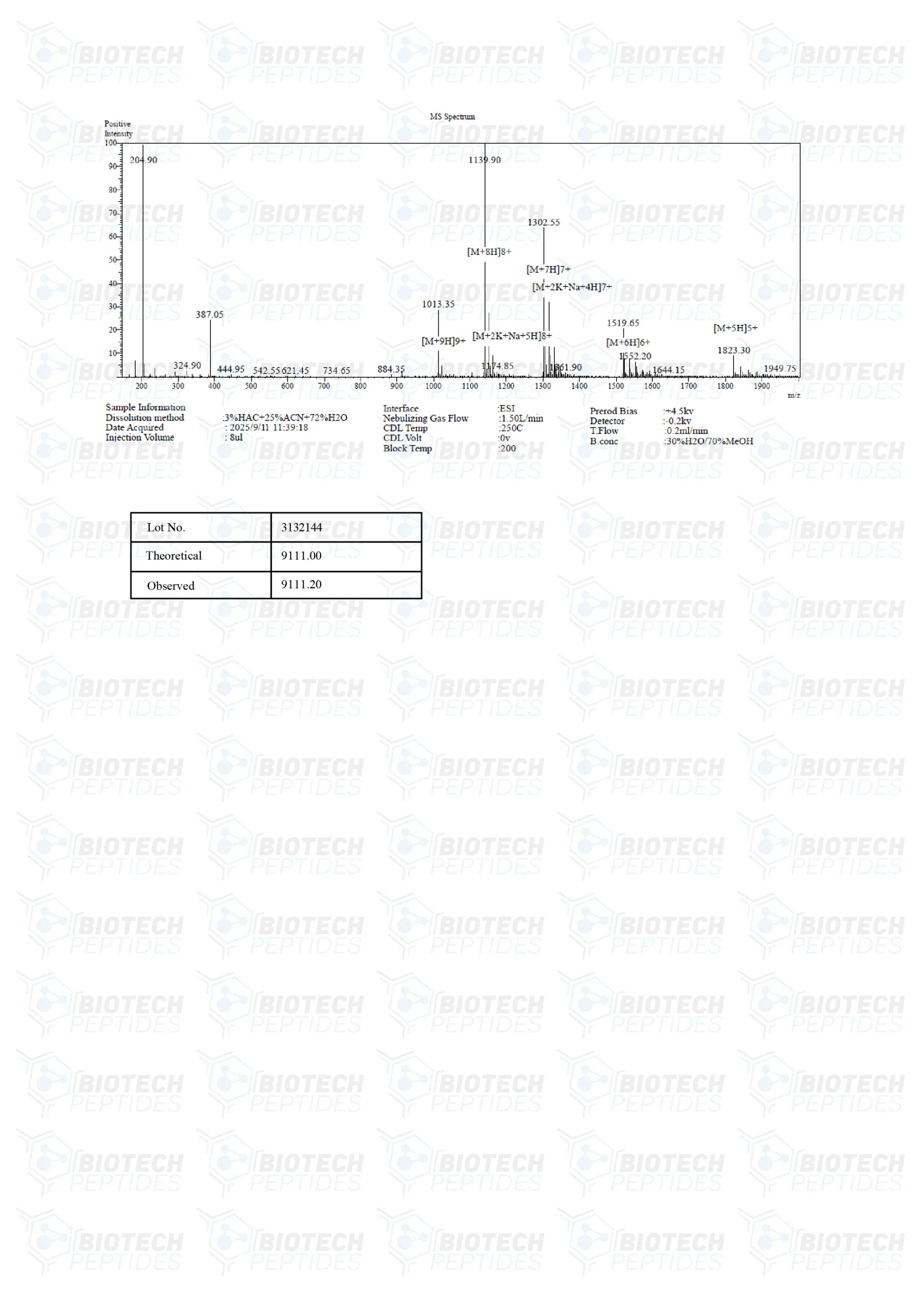
Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 Peptide
Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 is an altered variant of insulin-like growth factor-1; the complete name of the peptide is insulin-like growth factor-1 long arginine 3. IGF-1 derivatives have played important roles in research studies on cell proliferation, cell division, and cell-to-cell communication. Despite research reporting physiological potential similar to the parent protein, Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 does not appear to interact with IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) as strongly as IGF-1. IGFBPs are a group of proteins that modulate the accessibility of Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGFs) within the bloodstream. This modulation potentially alters how IGFs engage with diverse bodily tissues. A reduction in the binding affinity of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Long Arg3 (IGF-1 LR3) for IGFBPs might potentially influence its bioavailability. Furthermore, this reduced binding might also affect the manner in which IGF-1 LR3 interacts with targeted tissues within experimental frameworks. Such alterations may lead to an enhanced potential of IGF-1 LR3, albeit possibly with a diminished duration of its active presence. This scenario suggests that the dynamics between IGF-1 LR3 and IGFBPs might be critical in determining the functional outcomes of IGF-1 LR3 in specific experimental contexts. The structural modifications in IGF-1 LR3 may have also contributed to the increased affinity of the peptide towards the IGF-1 receptors. The peptide is created by the inclusion of 13 amino acids to the N-terminus of native IGF-1 and by replacing the glutamic acid at position 3 with arginine, which ultimately leads to the formation of an 83 amino acid peptide.[1] The designation of Receptor Grade addresses the purity of the reference product, which is considered higher than Media Grade IGF-1 LR3.
Specifications
Molecular Formula: C400H625N111O115S9
Molecular Weight: 9117.5 g/mol
Sequence: MFPAMPLSSL FVNGPRTLCG AELVDALQFV CGDRGFYFNK PTGYGSSSRR APQTGIVDEC CFRSCDLRRL EMYCAPLKPA KSA
Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 Research
Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 and Cell Division
Like IGF-1, research suggests that Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 may act as a stimulus for cell division and proliferation, primarily affecting connective tissues of the muscle and bone and cell division in the liver, kidney, skin, lung, nerve, and blood tissues. IGF-1 is best considered to be a maturation hormone because of its apparent influence in cell proliferation, differentiation, and maturation, helping them to carry out their specialized functions. The higher potency of Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 towards the IGF-1 receptors may make it the preferred molecule for studies involving cell division. Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 appears to provide almost three times as much cellular activation compared to similar IGF-1.[2] Notably, the researchers commented that analogs, including “LR3 IGF-1, were approx. 2.5-fold more potent than IGF-1” in enhancing anabolic activities in various experimental models. These activities included increased body mass, growth of visceral organs, and possibly improved feed utilization efficiency when models were continuously exposed to the agent. The implication is that IGF-1 LR3 might exhibit increased efficacy in studies focused on cellular proliferation compared to its unmodified counterpart, IGF-1. This research employed murine models subjected to catabolic stressors. The team noted a significant reduction in the excretion of Nτ-methylhistidine, an indicator of muscle protein breakdown. The decrease in this biomarker was more substantial with IGF-1 LR3, potentially up to threefold compared to IGF-1. This suggests that under certain experimental conditions, IGF-1 LR3 might exhibit more pronounced anabolic actions, though these were not consistently observed across all the variables measured. Given these findings, it might be suggested that Receptor Grade IGF-I LR3, specifically engineered for enhanced receptor affinity, might show even greater anabolic activity than IGF-1.
Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 and Myostatin
Myostatin (also known as growth differentiation factor 8) is a muscle protein that is considered to surpress the growth and differentiation of muscle cells. Myostatin may thus be deemed crucial in protection from unregulated hypertrophy. However, some situations demand inhibition of myosin. Blocking of myosin may be impactful in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) research, or in research related to muscle loss due to prolonged immobility. In such cases, blocking the natural enzyme might slow down muscle breakdown. Studies conducted in mouse models of DMD have suggested that Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 and other IGF-1 derivatives may overcome the adverse impacts of Myostatin to protect muscle cells and prevent apoptosis.[3] The scientists note that “results together suggest that myostatin suppresses both basal and IGF-1-stimulated proliferation of both WAT and BAT preadipocytes, actions that are again similar to those in muscle satellite cells.” Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3, due to its speculated stability, may potentially counteract Myostatin by activating MyoD, a muscle protein normally triggered through prolonged physical strain.
Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 and Metabolism
Researchers suggest that Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 may indirectly boost fat cell dissolution through association with the IGF-1R receptor and the insulin receptor. These interactions may improve glucose uptake from the blood by muscle, nerve, and liver cells. It is possible that the observed actions occurred through a complex signaling mechanism that involves the PI3K (Phosphoinositide 3-kinases) and AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) pathways. In this context, PI3K and AMPK are considered critical molecular pathways in cells, regulating various functions, including metabolism and growth. Specifically, it might be speculated that the interaction of IGF-1 analogs with their specific receptors might initiate a series of biochemical reactions via the PI3K pathway, posited as essential for cell proliferation and survival. This activation of the PI3K pathway could trigger Protein Kinase B (Akt), a potential enzyme within this pathway that may influence the movement of glucose transporters to the plasma membrane, potentially increasing the uptake of glucose by cells. Simultaneously, the AMPK pathway, which may play a significant role in maintaining energy homeostasis, might be indirectly affected by IGF-1 analogs such as IGF-1 LR3. The influence of these analogs may potentially alter AMPK activity, stimulating the cellular intake of glucose. Further, such activation may feasibly facilitate the movement of GLUT4 (Glucose Transporter Type 4), a predominant glucose transporter, to the cell surface, potentially promoting the entry of glucose into the cells. Overall, this potential may result in an overall reduction in blood sugar levels, which then triggers adipose tissue and the liver to initiate catabolism of glycogen and triglycerides. Overall, this may lead to decreased adipose tissue and net energy consumption (i.e. net catabolism). Given its potential in controlling blood sugar levels, Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 may reduce insulin levels and the need for exogenous insulin in diabetes.[4]
Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 and Longevity Research
Studies observe that Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 may promote tissue repair and cell survival, making it a potentially protective molecule against cellular damage. Research in cows and pigs indicates that Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 exposure may overcome the impacts related to cell turnover. Ongoing research in mice has focused on the potential of Receptor Grade IGF-1 LR3 in possibly mitigating the progression of a wide range of conditions such as muscle atrophy, dementia, and kidney disease.[5]
Disclaimer: The products mentioned are not intended for human or animal consumption. Research chemicals are intended solely for laboratory experimentation and/or in-vitro testing. Bodily introduction of any sort is strictly prohibited by law. All purchases are limited to licensed researchers and/or qualified professionals. All information shared in this article is for educational purposes only.
References
- Assefa B, Mahmoud AM, Pfeiffer AFH, Birkenfeld AL, Spranger J, Arafat AM. Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Binding Protein-2, Independently of IGF-1, Induces GLUT-4 Translocation and Glucose Uptake in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:3035184. doi: 10.1155/2017/3035184. Epub 2017 Dec 20. PMID: 29422987; PMCID: PMC5750484.
- Tomas FM, Knowles SE, Owens PC, Chandler CS, Francis GL, Read LC, Ballard FJ. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and especially IGF-I variants are anabolic in dexamethasone-treated rats. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 15;282 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):91-7. doi: 10.1042/bj2820091. PMID: 1371669; PMCID: PMC1130894.
- Li N, Yang Q, Walker RG, Thompson TB, Du M, Rodgers BD. Myostatin Attenuation In Vivo Reduces Adiposity, but Activates Adipogenesis. Endocrinology. 2016 Jan;157(1):282-91. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1546. Epub 2015 Nov 18. PMID: 26580671; PMCID: PMC4701895.
- Bailes J, Soloviev M. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) and Its Monitoring in Medical Diagnostic and in Sports. Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 4;11(2):217. doi: 10.3390/biom11020217. PMID: 33557137; PMCID: PMC7913862.
- AsghariHanjani N, Vafa M. The role of IGF-1 in obesity, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2019 Jun 17;33:56. doi: 10.34171/mjiri.33.56. PMID: 31456980; PMCID: PMC6708115.
- Philippou A, Barton ER. Optimizing IGF-I for skeletal muscle therapeutics. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2014 Oct;24(5):157-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2014.06.003. Epub 2014 Jun 19. PMID: 25002025; PMCID: PMC4665094.