Thymalin (25mg)
$114.00
Thymalin peptides are Synthesized and Lyophilized in the USA.
Discount per Quantity
| Quantity | 5 - 9 | 10 + |
|---|---|---|
| Discount | 5% | 10% |
| Price | $108.30 | $102.60 |
FREE - USPS priority shipping
Thymalin Peptide
Thymalin, sometimes referred to as Thymalin Alpha-1, is the synthetic variant of the endogenous Thymulin, which was first isolated from the thymus in 1977. The endogenously produced Thymalin has been researched for its potential in a wide landscape of research areas, with its influence speculated to extend to regulatory action on inflammation, mitigation of pain perception, neuroprotective action, and immune function support. Early studies have suggested that Thymalin and other thymus and pineal gland secretions may also support cell longevity.
Specifications
Other Known Titles: Nonathymulin, Thymic Factor, Serum Thymic Factor, Thymalin Alpha 1
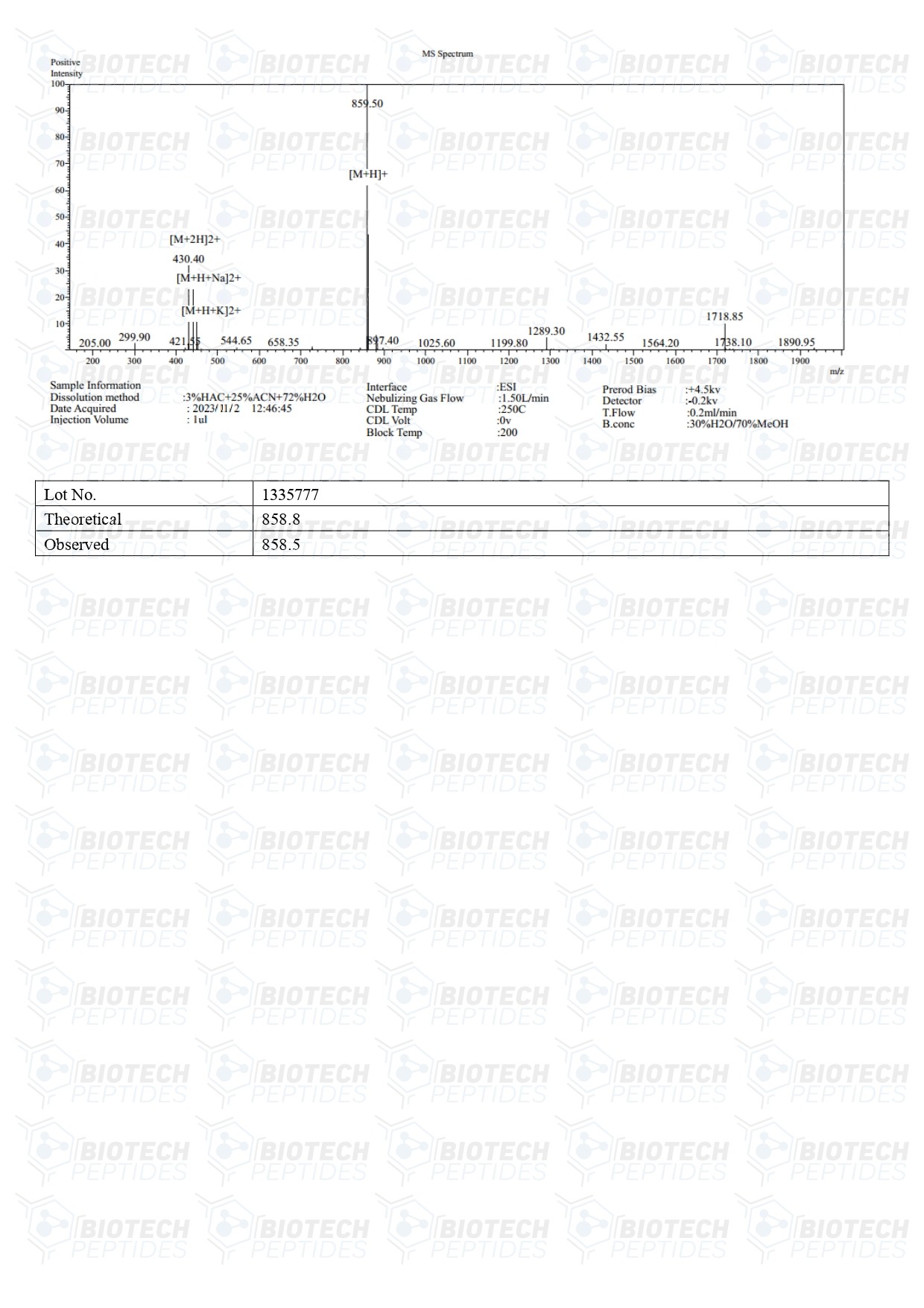
Molecular Formula: C33H54N12O15
Molecular Weight: 858.86 g/mol
Sequence: Pyr-Ala-Lys-Ser-Gln-Gly-Gly-Ser-Asn
Thymalin Research
Thymalin and Cell Longevity
Research findings in Russia at the beginning of the 21st century led scientists to hypothesize that Thymalin may potentially normalize various baseline functions. The study reported improved cardiovascular, immune, and nervous system function tentatively linked to peptide exposure in murine models. Overall, a significant reduction in acute respiratory disease, hypertension, osteoporosis, ischemic heart disease, and symptoms of arthritis was indicated. The models exposed to Thymalin throughout the study exhibited an apparent 2-fold reduction in mortality rate compared to controls.[1] Thymalin appears to act synergistically with certain thymic and pineal gland isolates, potentially controlling mortality rate by up to 4-fold when combined with Epithalmin. Both the thymus and pineal glands are associated with cellularl aging. During optimal functioning, the pineal gland is considered to protect the thymus from the degenerative action of aging cells.
Thymalin and Immune System Functionality
Thymalin studies suggest the peptide may potentially modify cellular immunity and levels of lymphocytes and may thereby regulate T-cell differentiation and natural killer (NK) cell activity. It may be relevant in research within the context of chronic conditions like diabetes, which tend to diminish immune support. Researchers have suggested that the peptide may potentially improve immune correction, T cell proliferation, and control of retinal inflammation. In research within the context of diabetes, it was speculated to also reduce the progression of diabetic retinopathy.[2] This same characteristic is suggested in chronic immunodeficiency/immune dysregulation in cases of HIV. Research studies in murine models employing the combination of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) and Thymalin appeared to have mitigated or reversed damage to the immune system and improved the numbers of CD4+ T-cells in the examined HIV models. Additional studies indicated that the peptide may have mitigated the onset of physiological changes, improved immune function, and lowered the outcome of infection following the surgical removal of the thymus. The rats reportedly exhibited a decline in thymic function, weight loss, and a decrease in cell proliferation.
Nonathymulin Research and Cancer
Research in mice suggests that Thymalin may act synergistically with pulsed laser radiation studied in the context of certain types of cancer. Neodymium lasers are frequently used to mitigate and prevent cancerous and precancerous skin lesions (including melanoma) with moderate to high success rates. The technique is considered to be employed specifically in cases of metastasis. A combination of Thymalin and radiation may be synergistic as the peptide appears to impact the number of antibody-producing cells in the spleen. It is thought that this may have a greater suppressive impact on the tumor and attain higher remission rates. Studies suggest Nonathymulin may exhibit activity without the synergistic action of radiation. Research in rats observed that sub-therapeutic concentrations of the molecule appeared to block tumor growth in nearly 80% of examined cases and tumor regression in more than half of the animals in the experiment.[3] According to the researchers, the “High efficiency of Thymalin can be attributed to the use of lower [concentrations] of the substance and their modulation during the [exposure] course in accordance with the regimes of activation therapy.” The peptide, when combined with plasmapheresis, exhibited potential for action against chronic lympholeukemia. The peptide/plasmapheresis combination appears to engage in hematological compensation, potentially more than standard chemotherapeutic compounds. The combination also appeared to improve lymphoid activity.
Thymalin and Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a specific inflammatory condition of the skin and joints. A combination of standard compounds for psoriasis with Thymalin has yielded improved laboratory measures of the condition.[4] Researchers have suggested that Thymalin may have a measurable, observable influence on the status of the disease.
Thymalin and Tuberculosis Research
Research models of progressive pulmonary tuberculosis underwent either a standard antibiotic control procedure, or an antibiotic procedure with the addition of Thymalin influence. The group receiving Thymalin was observed to hold a higher recovery rate than the control cohort. Customizing the combination in each model resulted in a reported ~95% cure rate.[5] The peptide may have potential in research studies of compound-resistant tuberculosis. The cases of low T cell count and inferior blast transformation are considered to exhibit poor cellular immunity, which may be further aggravated in combination cases of diabetes. The peptide has been employed in studies related to these cases, with initial mitigatory findings.
Thymalin and Kidney Disease
Thymalin has been studied for its potential to improve the overall biological condition of research models of inflammatory kidney disease and chronic glomerulonephritis. In one Russian research study, the peptide was reported to support kidney function and blood indices of inflammation.[6] Researchers reported a betterment of immunity, which appeared to have led to reduced kidney damage and delayed chances of dialysis/kidney transplant.
Thymalin and Circadian Rhythm Disturbances
Studies in rats have suggested that thymic factor alterations may induce changes in circadian rhythms, leading to modified immunity. Seasonal changes in the day-night cycle may vary the peak levels of thymus function, thereby suppressing the immune system. Therefore, the antibody levels may become modified. Studies suggested that peptide exposure did not appear to reset the circadian changes but rather appeared to have boosted immune depletion.[7] The researchers noted that “The chronic (18 mo) administration of thymus preparation thymalin increased FTS titer and promoted the appearance of the peak of antibodies” suggesting the peptide may exhibit supportive activity in preventing infection.
Thymalin and Atherosclerosis Mechanisms
As per research in rabbits, the peptide appears to potentially regulate lipid levels and mediate plaque removal from the arterial wall by lymphocytes. More specifically, Thymalin displayed potential hypolipidemic (lipid-lowering) actions, suggesting that it might reduce lipid levels in the bloodstream. Concurrently, the study indicates that Thymalin also exhibited antiatherosclerotic actions. This term implies that Thymalin may possibly support in reducing or inhibiting the development of atherosclerotic plaques, which are buildups of fat cells, cholesterol, and other substances in and on the artery walls. Thymalin may normalize T-cell suppressor activity and sensitivity, thus controlling or abolishing the immune dysfunction causing plaque formation.[8] T-suppressor cells are a type of immune cell that is considered to regulate immune responses, including those involved in inflammatory processes such as atherosclerosis. Enhanced sensitivity to atherogenic lipoproteins usually indicates an increased inflammatory response to these molecules, which are considered critical in the development of atherosclerotic lesions. Thymalin apparently normalized T-suppressor cell activity and sensitivity to atherogenic lipoproteins. In short, Thymalin peptide may have the potential to overcome the dysfunction due to which immunity cannot control the onset of certain cardiac diseases.
Thymalin and Inflammation
Periodontitis is an inflammation of the gums and the allied oral structures. Nonathymulin has been studied for its potential influence in the reduction of inflammation and bacterial infections.[10] Severe emaciation may be induced by varying degrees of circulating thyroid hormones, and immune function and peripheral lymphocyte prevalence may be compromised. Thymalin exposure in animal models appeared to reverse thymic atrophy in this backdrop.[11] These cases may require zinc supplementation as well to facilitate Thymalin activity, as researchers suggest the peptide function may be regulated by zinc.
Furthermore, speculative studies indicate that Immune function may be influenced by Thymalin exposure. Research studies examining the actions of the peptide have suggested that it may improve T cell function and thus various aspects of cellular immunity, such as infection, inflammation, cancer, and cardiac disease.
Thymalin and Metabolism
In a comprehensive study spanning 6 to 8 years, the metabolic potential of Thymalin, a synthetic peptide analog of a naturally occurring thymic hormone, was explored using 266 mature test models, with a placebo as a control for comparison.[12] The investigation suggested that Thymalin might influence several basic physiological functions, potentially including those related to cardiovascular, neurological, and immunological systems within these research models. The study cautiously indicated that both metabolic rates and hemostasis—the process to stop bleeding—might have been favorably affected by Thymalin. It was hypothesized that Thymalin might play a role in sustaining or perhaps even revitalizing thymic functions, which are considered to diminish gradually.
This influence on thymic functions might, hypothetically, account for the noted enhancements in T-cell-mediated immunity. T-cells, pivotal in adaptive immunity, were observed to possibly show restoration in both quantity and functionality in models exposed to Thymalin. Moreover, the research explored Thymalin's potential actions on systemic inflammation, which is commonly observed upon maturation of the organism. Preliminary results hinted at a potential reduction in markers associated with systemic inflammation in the Thymalin-exposed models, suggesting that it might modulate cytokine production and immune cell regulation, potentially leading to a decrease in chronic inflammation. The influence of Thymalin on stress hormones, particularly cortisol—integral to the stress response—was another focal point. The study speculated that Thymalin might influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which oversees cortisol regulation, possibly leading to more stable cortisol levels and a reduction in the adverse actions associated with stress. In terms of metabolic function, there were observations of possible improvements in metabolic stability among the cohort exposed to Thymalin. Changes that might indicate normalization of metabolic parameters, such as glucose levels and lipid profiles, were noted, suggesting a potential influence of Thymalin on metabolic processes, possibly through the enhancement of cellular metabolism or direct actions on metabolic enzymes.
Thymalin and Cellular Aging Rate
In an investigative study focusing on matured murine models, researchers reported a differential in average lifespan: 949 days for the control group versus 1048 days for the Thymalin-exposed group.[13] Additionally, the 'aging rate'—a metric indicating the pace at which signs of biomarkers of cellular aging appear—was observed to be 0.0071 days in the control group compared to 0.0041 days in the Thymalin group. Further, the occurrence of tumor cells was reduced by approximately 1.5 times in the Thymalin group compared to the control group. This reduction was even more significant in the context of hematopoietic cancer cells, where tumor cell incidence was roughly 3.4 times lower in the Thymalin-exposed murine models. The researchers posit that Thymalin might potentially modify key aspects of the immune system considered crucial for cell regulation, and prevention of cancer cell development and subsequent spread of such cells. Further investigations might elucidate that the amino acids L-Glutamate (L-Glu) and L-Tryptophan (L-Trp), constituents of Thymalin, may play a role in the improved differentiation of T-cells. T-cells are considered to be vital components of the adaptive immune system, specifically adept at identifying complexes formed by peptides and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, crucial for initiating an immune response. The study also noted alterations in cyclic nucleotide levels, which are significant in cell signaling pathways. Enhanced activities in neutrophil chemotaxis and phagocytosis were observed, which are fundamental to the organism’s primary defense against pathogens and possibly malignant cells.
Disclaimer: The products mentioned are not intended for human or animal consumption. Research chemicals are intended solely for laboratory experimentation and/or in-vitro testing. Bodily introduction of any sort is strictly prohibited by law. All purchases are limited to licensed researchers and/or qualified professionals. All information shared in this article is for educational purposes only.
References
- Khavinson, V. K.h, & Morozov, V. G. (2003). Peptides of pineal gland and thymus prolong human life. Neuro endocrinology letters, 24(3-4), 233–240.
- Zhaboiedov, H. D., Bychkova, N. H., Skrypnik, R. L., & Sydorova, M. V. (2001). Doslidzhennia stanu klitynnoho i humoral’noho imunitetu ta vyznachennia indyvidual’noï chutlyvosti T-limfotsytiv do imunokorektoriv u khvorykh s diabetychnoiu retynopatiieiu [Evaluation of cellular and humoral immunity and individual sensitivity of T-lymphocytes to immunocorrectors in patients with diabetic retinopathy]. Likars’ka sprava, (1), 53–56.
- Zhukova, G. V., Schikhlyarova, A. I., Barteneva, T. A., Shevchenko, A. N., & Zakharyuta, F. M. (2018). Effect of Thymalin on the Tumor and Thymus under Conditions of Activation Therapy In Vivo. Bulletin of experimental biology and medicine, 165(1), 80–83. doi:10.1007/s10517-018-4104-z.
- Isaeva, M. P., Budazhabon, G. B., & Kuznik, B. I. (1989). Vliianie timalina na pokazateli immuniteta i gemostaza u bol’nykh rasprostranennymi formami psoziaza [The effect of thymalin on indices of immunity and hemostasis in patients with disseminated forms of psoriasis]. Vestnik dermatologii i venerologii, (10), 42–43.
- Maslennikov, A. A., Kamenev, V. F., & Kolomiets, V. M. (2007). Problemy tuberkuleza i boleznei legkikh, (9), 30–33.
- Budazhabon, G. V., Kuznik, B. I., Morozov, V. G., Orlova, N. N., & Khavinson, V. K.h (1984). Sostoianie immunogeneza i gemostaza u bol’nykh s obostreniem khronicheskogo glomerulonefrita, lechennykh timalinom [Immunogenesis and hemostasis in patients with exacerbated chronic glomerulonephritis treated with thymalin]. Terapevticheskii arkhiv, 56(10), 62–66.
- Labunets’ I. F. (2001). Vikovi zminy tsyrkadnykh i tsyrkanual’nykh kolyvan’ velychyny imunnoï vidpovidi ta chysla klityn u limfoïdnykh orhanakh tvaryn: mozhlyvyĭ zv’iazok z faktoramy tymusa [Age-related changes in circadian and circannual fluctuations of the immune response and the number of cells in lymphoid organs of animals: a possible connection to thymic factors]. Fiziolohichnyi zhurnal (Kiev, Ukraine : 1994), 47(5), 54–62.
- Ryzhenkov, V. E., Ogurtsov, R. P., Trubacheva, V. V., Popov, V. G., & Puzyreva, V. P. (1988). Vliianie timalina na razvitie éksperimental’noĭ giperlipidemii i ateroskleroza [Effect of thymalin on the development of experimental hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis]. Voprosy meditsinskoi khimii, 34(1), 51–56.
- Zhumadilov, Z.hS.h, & Terekhova, R. P. (1985). Primenenie timalina dlia profilaktiki posleoperatsionnykh gnoĭno-vospalitel’nykh oslozhneniĭ [Use of thymalin for preventing postoperative suppurative and inflammatory complications]. Klinicheskaia khirurgiia, (1), 36–38.
- Kuznik, B. I., Khavinson, V. K.h, Morozova, V. G., Budazhabon, G. B., & Budazhabon, N. G. (1985). Primenenie timalina dlia lecheniia bol’nykh parodontitom [Use of thymalin in treating periodontitis patients]. Stomatologiia, 64(1), 20–22.
- Wade, S., Bleiberg, F., Mossé, A., Lubetzki, J., Flavigny, H., Chapuis, P., Roche, D., Lemonnier, D., & Dardenne, M. (1985). Thymulin (Zn-facteur thymique serique) activity in anorexia nervosa patients. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 42(2), 275–280. doi:10.1093/ajcn/42.2.275.
- Khavinson VKh, Morozov VG. Peptides of pineal gland and thymus prolong human life. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2003 Jun-Aug;24(3-4):233-40. PMID: 14523363.
- Anisimov VN, Khavinson VK, Morozov VG. Immunomodulatory synthetic dipeptide L-Glu-L-Trp slows down aging and inhibits spontaneous carcinogenesis in rats. Biogerontology. 2000;1(1):55-9.