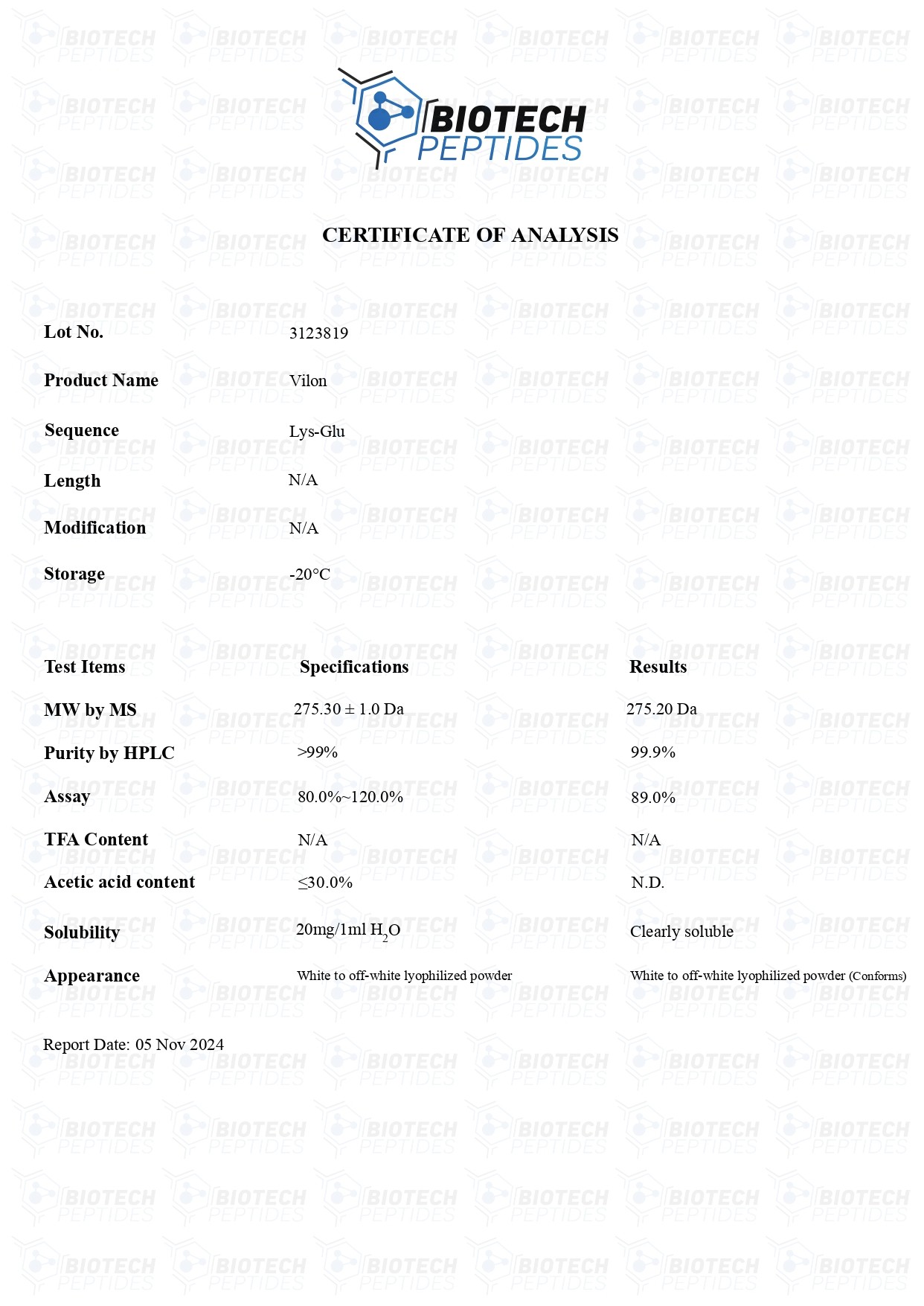
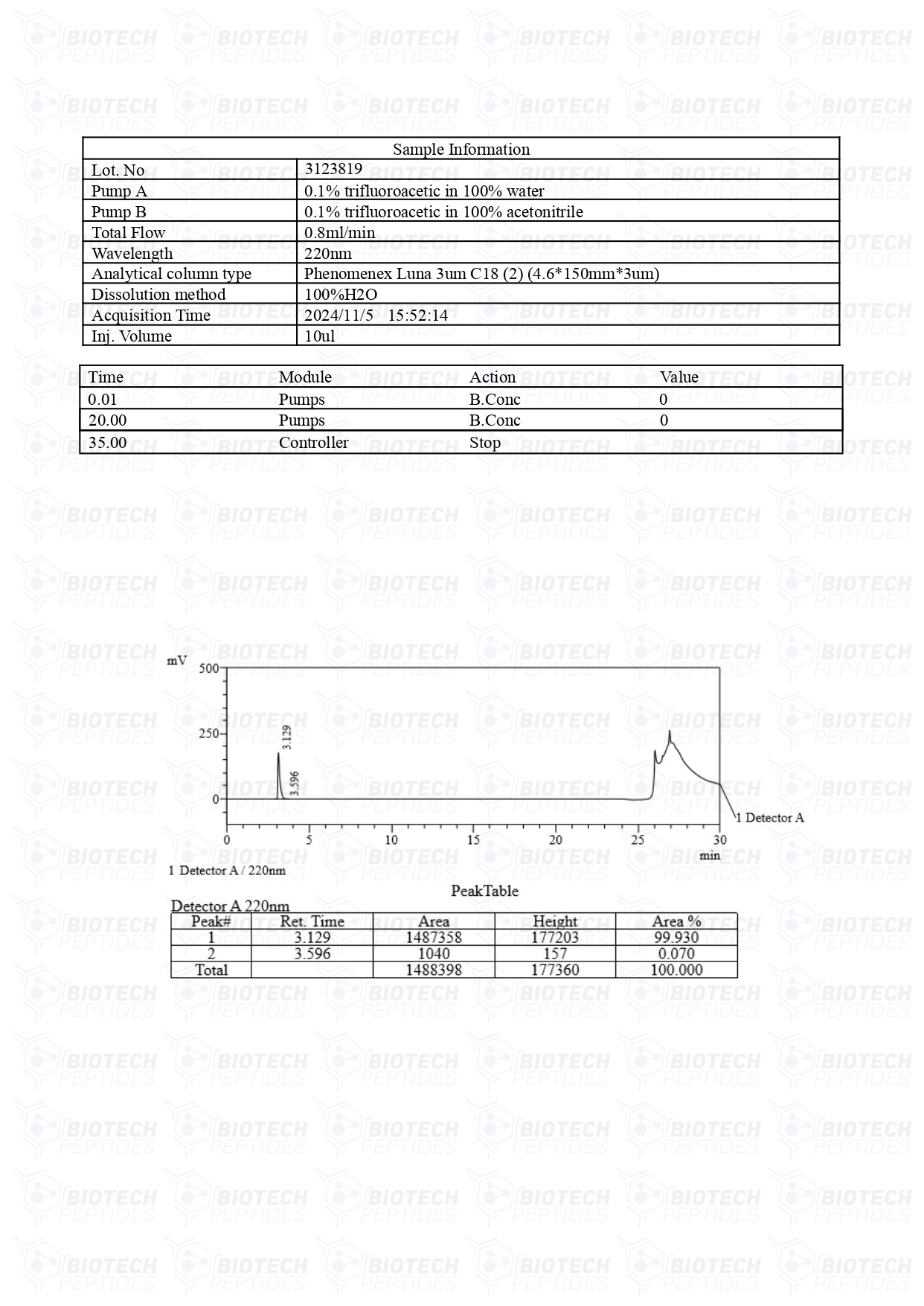
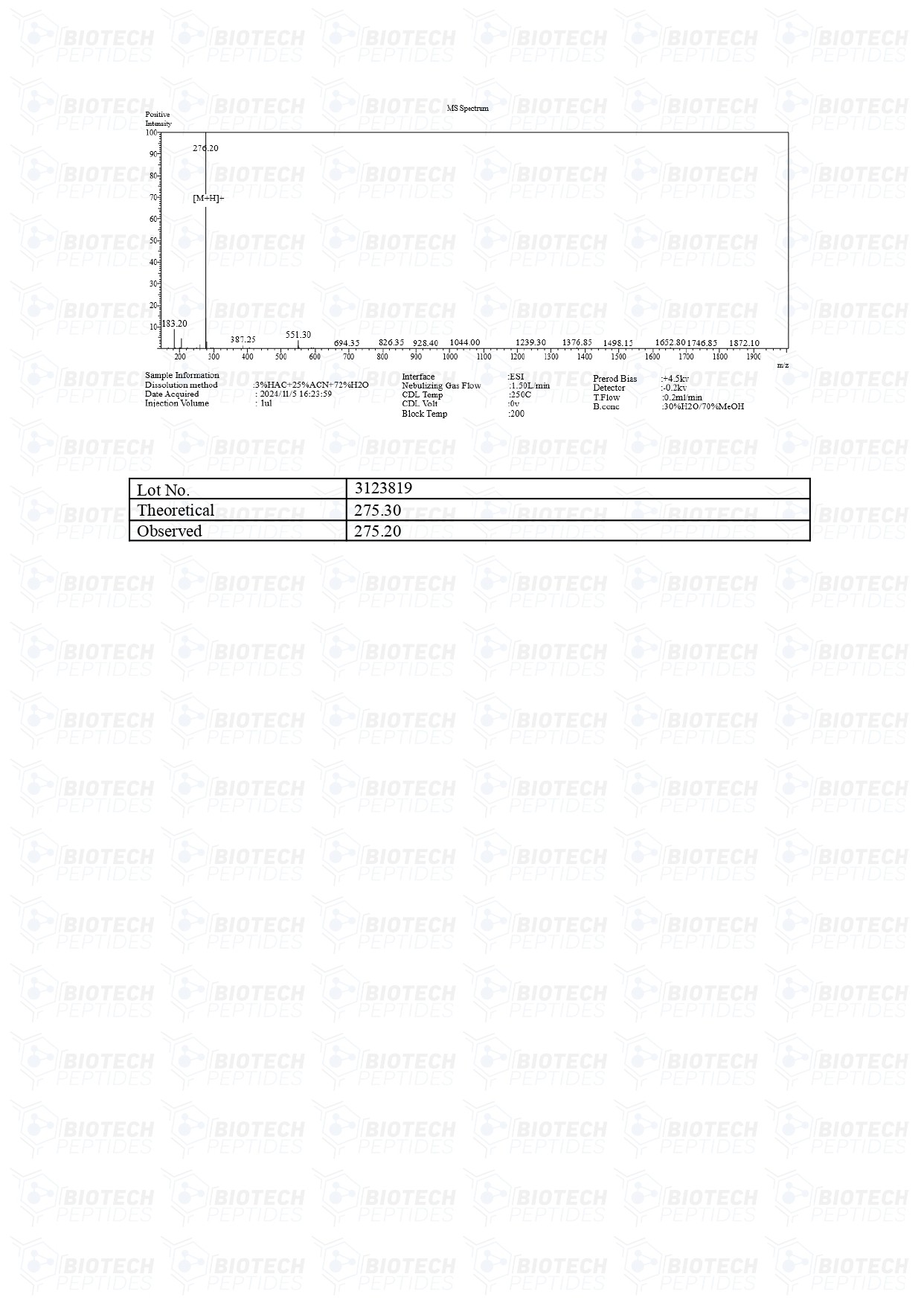
Vilon (20mg)
Original price was: $65.00.$61.00Current price is: $61.00.
Vilon peptides are Synthesized and Lyophilized in the USA.
Discount per Quantity
| Quantity | 5 - 9 | 10 + |
|---|---|---|
| Discount | 5% | 10% |
| Price | $57.95 | $54.90 |
FREE - USPS priority shipping
Vilon Peptide
Vilon (or Lyslglutamic Acid) is a peptide with apparent immunomodulatory and anti-aging bioregulation potential. It is a short peptide with just two amino acids in length. Scientific research suggests it may potentially act to regulate the vascular system and encourage hemostasis. Its functions may be more widespread, with studies indicating its possible influence in reducing the prevalence and growth of spontaneous tumors. Advocate researchers like Dr. Vladimir Anisimov believe that the peptide may become more widespread in contemporary research within the context of geroprotection.
Specifications
Sequence Formula: H-Lys-Glu-OH
Molecular Formula: C11N21N3O5
Molecular Weight: 257.30g/mol
Synonyms: Lysylglutamate, normophthal, Lyslglutamic acid
Vilon Research
Vilon Peptide and Cancer Cells
Vilon, according to research findings in murine models, may reduce the prevalence of cancer cells. Studies report that exposure to the peptide may potentially have reduced tumor prevalence and inhibited growth in mice, suggesting that Vilon may warrant further examination within the context of chemotherapeutic research, as outlined below.[1]
Scientific studies reported negative results when Vilon was combined with a platinum-based chemotherapeutic agent. The anti-cancer potential of Vilon and its potential within chemotherapy research is still under investigation, and studies are not yet conclusive. The scientists revealed that “Vilon stimulated apoptosis both in young and old rats, but the inhibitory effect of cyclophosphan was abolished in the presence of vilon in culture media.”[2]
Further research investigated the potential impact of Vilon against a placebo on urinary bladder cancer cell dynamics in murine models exposed to N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine (BBNA). This compound may trigger bladder cancer cell formation.[3] Initial results indicate that Vilon may reduce the emergence of cancer cells, with 56% of the Vilon-exposed murine models showing cancer cell development compared to 75.5% in the control group. These findings imply that Vilon might modulate cancer cell evolution in the presence of BBNA. The study also observed potential changes in the bladder mucosa of the Vilon-exposed murine models, including reduced frequency and severity of early cancerous and pre-cancerous alterations. Notably, there were fewer instances of hyperplasia—an abnormal increase in cell numbers—and a slower rate of malignant transformation, suggesting Vilon's potential to delay or alter the transition of cells from normal to malignant states. Further, the average number of tumors per Vilon-exposed mouse was lower (1.5) compared to the control group (2.6), and the tumor cells displayed a less aggressive growth pattern. These observations imply that Vilon might interfere with the cancer-promoting mechanisms of BBNA. Thus, the data suggest that Vilon might act as an immunomodulator, potentially inhibiting the initiation and progression of cancer in this model.
Vilon Peptide and Immunity
Studies in Vilon expression suggest that it may be a potent chromatin structure regulator.[4] Studies reported that Vilon exposure may lead to potential activation of chromatin unrolling, release of repressed genes, and activation of synthetic processes through the reactivation of ribosomal genes in the unrolled chromatin. It does not appear to cause structural chromatin decondensation.
The research that led to the development of these hypotheses further suggests that Vilon may induce the reactivation of silenced DNA genes. Generally, Chromatin presents as heterochromatin and euchromatin. Genes in the heterochromatin aspect of DNA are considered to be inaccessible to the production of proteins. The condensation of Chromatin may occur due to cellular aging and senescence, and points to why cells and tissues lose functionality over time. The possible ability of Vilon in symbiosis with other peptide bioregulators to reactivate specific genes by unrolling heterochromatin may improve immune function in aged animal models.[5] The researchers reported that “peptide bioregulators Epitalon, Livagen, and Vilon [may] cause activation (deheterochromatinization) of chromatin in lymphocytes of [older research models].”
Furthermore, Interleukin-2 may be vital in immune response coordination to microbial infection, as it may inhibit the prevalence of autoimmune reactions. The activation of interleukin-2 signaling is one suggested action of Vilon peptide in the spleen. Vilon may reinstate the immune system to a more effective state and potentially activate lymphocytes and splenocytes—boosting natural prevention against the prevalence of autoimmune reactions.
Vilon, according to research, may enhance the propagation of CD5 T-cells in the thymus. CD5 is a potent immunohistochemical marker for T-helper cells and cytotoxic CD8 T-cells found on the surface of certain immune cells and may play a significant role in the growth and differentiation of T-cells within the thymus.[6] The researchers observed an apparent rise of 78% in CD5 expression in thymic cells derived from murine models, and a 45% elevation in cells taken from embryonic thymus, when compared to the baseline figures recorded in the control specimens. The research suggests that Vilon might impact the differentiation processes in thymic cells. This may guide the precursors of T-cells toward differentiating into CD4+ T-helper cells. These CD4+ T-helper cells are considered crucial elements of the adaptive immune system, supporting and orchestrating responses of other immune cells. Thus, it is hypothesized that Vilon's action might influence the immune system and prevent the prevalence of autoimmune reactions. Vilon appears to function only to reactivate the immune system through genes that have been silenced via Chromatin changes. It doesn’t appear to actuate genes that would be silent in the cells it modifies.
Vilon Peptide and the Kidneys, Heart
Vilon’s impact on vasculature hasn’t been well studied, but some research data suggests that it may exhibit action within these organs. Research in murine models posits that Vilon may alter more than 36 gene expressions in the heart. Combined with Epitalon, this number was reported to elevate to 144 genes. These results indicate that Vilon may influence gene expression trends in the cardiovascular system, improving hemodynamic function. Research suggests that Vilon may reduce concentrations of TGF-beta 1 in the kidneys and highly vascular organs, allowing for permeability of microvessels.[7] The final result may be increased hemostasis during kidney failure, positing that Vilon may impact the vascular system. Research in research models of diabetes reports that Vilon (Lyslglutamic Acid) may bolster coagulation by enhancing the antithrombin III anticoagulant levels and Protein C, even as it stimulates fibrinolysis. The consequence of this may be lessened blood clots in clotting-prone conditions.[8]
Vilon Peptide and Cellular Aging
Exposure to the Vilon peptide appears to enhance contractile force and endurance within muscle tissues even as it potentially decreases the prevalence of cancer cells. In murine models, these two apparent peptide functions were hypothesized to have extended overall muscle cell longevity. According to research, the exposure of Vilon in early developmental stages may have increased the longevity of the animal research models under observation. The hypothesis holds that the introduction of Vilon in later stages may reverse senescence in existing cells but may not do the same for cells discarded via apoptosis. In the same sense, the early exposure of Vilon in murine models may have increased a degree of protection, with modification lowered. Consequently, many cells may remain stable and viable for extended periods, retaining limited stem cell lines.[9] Another study has explored the potential of Vilon on tissue explants from murine models at various life stages—neonatal, juvenile, and mature.[10] The study speculates that Vilon might help preserve tissue structure and potentially boost the cells' regenerative abilities and overall function. Notably, its impact appears more pronounced in tissues from older mice, suggesting that Vilon could be crucial for cellular aging and regeneration research. This raises the possibility that Vilon may adjust or stabilize age-related cellular functions in older tissues. Further research has investigated Vilon’s capability to mitigate the accelerated aging in murine thymus and spleen induced by low levels of ionizing radiation.[11] Preliminary results tentatively suggest that Vilon might partially counteract the aging actions of radiation. This insight positions Vilon as a valuable compound for further exploration in studies aimed at managing radiation-driven cellular aging in key immune organs like the thymus. The findings emphasize the importance of Vilon in preserving organ functionality under radiative stress, hinting at strategies for addressing radiation-induced cellular deterioration.
Vilon’s anti-aging hypothesis is multifaceted—extending to gastrointestinal (GI) functions, where it appears to support the enzyme activity in the GI tracts of aged murine models. It also may improve the cell barrier functions—reducing the prevalence of leaky gut, and increasing resistance to diseases. Vilon may mitigate nutrient extraction by enhancing glucose and glycine absorption, improving overall cell function and extending longevity. According to research by Dr. Vladimir N. Anisimov, two glands, the thymus and pineas, are vital regulators of cell aging.[12] It is important to note that Vilon is classified as a thymic peptide and appears to act on lymphocytes and other cells produced in the thymus.
Disclaimer: The products mentioned are not intended for human or animal consumption. Research chemicals are intended solely for laboratory experimentation and/or in-vitro testing. Bodily introduction of any sort is strictly prohibited by law. All purchases are limited to licensed researchers and/or qualified professionals. All information shared in this article is for educational purposes only.
References
- Khavinson VKh, Anisimov VN. A synthetic dipeptide vilon (L-Lys-L-Glu) inhibits growth of spontaneous tumors and increases life span of mice. Dokl Biol Sci. 2000 May-Jun;372:261-3. PMID: 10944717.
- Barykina OP, Iuzhakov VV, Chalisova NI, Kvetnoĭ IM, Konovalov SS. Sochetannoe vliianie vilona i tsiklofosfana na transplanty opukholeĭ i éksplantaty limfoidnoĭ tkani mysheĭ i krys raznogo vozrasta [Combined effect of vilon and cyclophosphane on tumor transplants and lymphoid tissue explants in mice and rats of various age]. Adv Gerontol. 2003;12:128-31. Russian. PMID: 14743610.
- Pliss GB, Mel'nikov AS, Malinin VV, Khavinson VK. Inhibitory effect of peptide vilon on the development of induced rat urinary bladder tumors in rats. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2001 Jun;131(6):558-60. doi: 10.1023/a:1012354603132. PMID: 11586406.
- Lezhava T, Khavison V, Monaselidze J, Jokhadze T, Dvalishvili N, Bablishvili N, Barbakadze S. Bioregulator Vilon-induced reactivation of chromatin in cultured lymphocytes from old people. Biogerontology. 2004;5(2):73-9. doi: 10.1023/B:BGEN.0000025070.90330.7f. PMID: 15105581.
- Lezhava T, Monaselidze J, Kadotani T, Dvalishvili N, Buadze T. Anti-aging peptide bioregulators induce reactivation of chromatin. Georgian Med News. 2006 Apr;(133):111-5. PMID: 16705247.
- Sevostianova NN, Linkova NS, Polyakova VO, Chervyakova NA, Kostylev AV, Durnova AO, Kvetnoy IM, Abdulragimov RI, Khavinson VH. Immunomodulating effects of Vilon and its analogue in the culture of human and animal thymus cells. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2013 Feb;154(4):562-5.
- Gavrisheva NA, Malinin VV, Ses TP, Kozlov KL, Panchenko AV, Titkov AY. Effect of peptide Vilon on the content of transforming growth factor-beta and permeability of microvessels during experimental chronic renal failure. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2005 Jan;139(1):24-6. doi: 10.1007/s10517-005-0202-9. PMID: 16142267.
- Kuznik BI, Isakova NV, Kliuchereva NN, Maleeva NV, Pinelis IS. [Effect of vilon on the immunity status and coagulation hemostasis in patients of different age with diabetes mellitus]. Adv Gerontol. 2007;20(2):106-15. Russian. PMID: 18306698
- Anisimov VN, Loktionov AS, Khavinson VK, Morozov VG. Effect of low-molecular-weight factors of thymus and pineal gland on life span and spontaneous tumour development in female mice of different age. Mech Ageing Dev. 1989 Sep;49(3):245-57. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(89)90075-4. PMID: 2682058.
- Kniaz'kin IV, Iuzhakov VV, Chalisova NI, Grigor'ev EI. Funktsional'naia morfologiia organotipicheskoĭ kul'tury selezenkoi krys razlichnogo vozrasta pri deĭstvii vilona [Functional morphology of organotypic culture of spleens from rats of various ages exposed to vilon]. Adv Gerontol. 2002;9:110-5. Russian. PMID: 12096432.
- Kniaz'kin IV, Poliakova VO. Deĭstvie vilona na timus i selezenku v radiatsionnoĭ modeli prezhdevremennogo stareniia [The effect of vilon on the thymus and spleen in a radiation model of premature aging]. Adv Gerontol. 2002;9:105-9. Russian. PMID: 12096431.
- Anisimov VN, Khavinson VKh. [The use of peptide bioregulators for cancer prevention: results of 35 years of research experience and perspectives]. Vopr Onkol. 2009;55(3):291-304. Russian. PMID: 19670728.