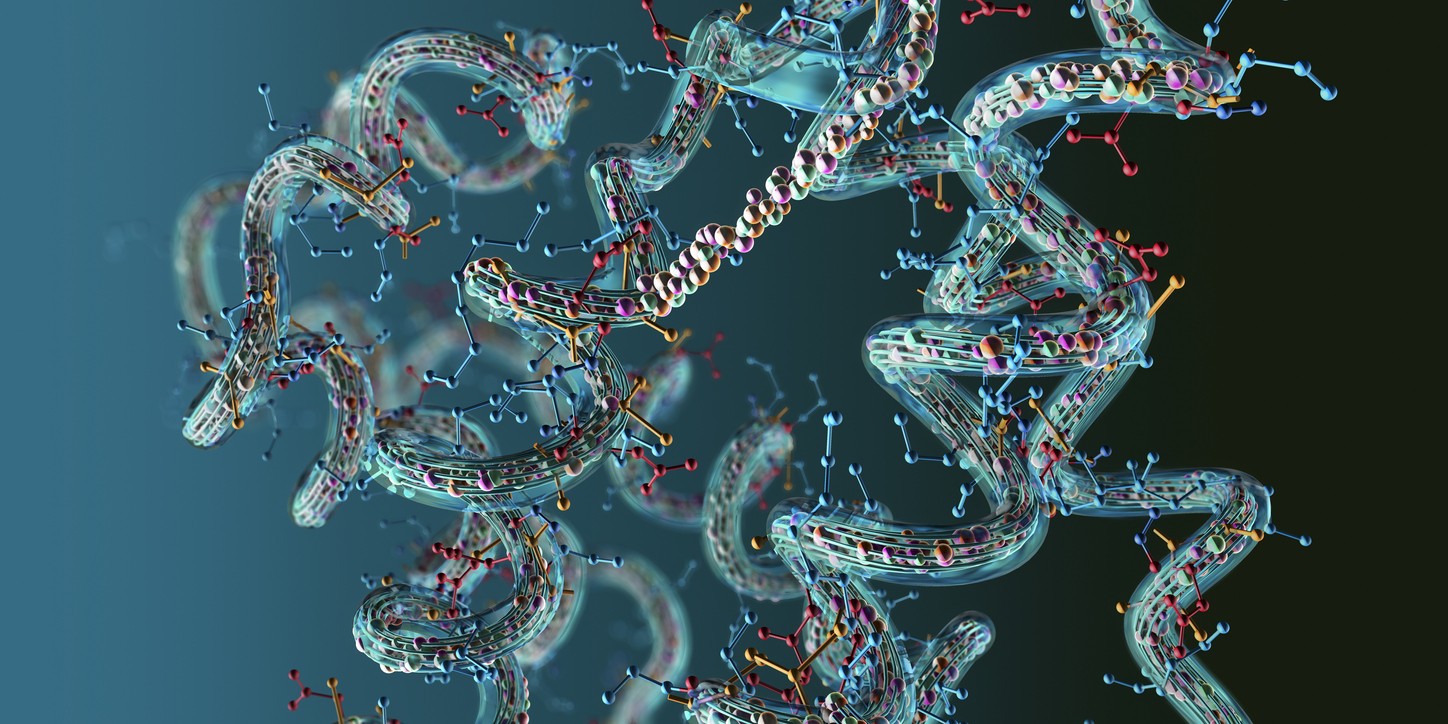
Therefore, peptides may basically be described as smaller, simpler versions of proteins. Studies have suggested that they may affect immunomodulation, growth hormone release, extracellular matrix production, and nerve cell growth and migration. Peptides may be the key to starting and stopping important biochemical cascades and may therefore prove important for biological function.
Studies over the last few decades have suggested that peptides may act to regulate cell aging cycles, control inflammation, mitigate infection, facilitate progressive tissue repair, increase cognitive synapses, and alter body composition.
Peptide Research
Slowing Cell Aging
A handful of peptides, including Sermorelin and Epithalon, have been suggested to alter the cell aging cycle at the DNA level. These have been speculated to activate an enzyme called telomerase to protect and repair DNA endpoints (called telomeres). Telomere degradation over time is one of the major signals that cells use to determine whether they divide and grow.Cell division may stop if telomeres become too short, and tissues may deteriorate. Certain peptides have been researched for their potential to delay the rate of tissue destruction by protecting telomeres. They may also reduce oxidative damage. Such peptides include Sermorelin, Epithalon, Ipamorelin, CJC-1295, and BPC 157. These peptides are classified as antioxidants that may mitigate cancer cell proliferation, cardiac and cognitive dysfunction, and other conditions.
Rapid Tissue Repair
Peptides may improve wound healing by affecting the growth hormone axis, increasing cell migration rates, reducing inflammation, and deposition extracellular matrix components. Many peptides, such as VIP, KPV, BPC 157, Sermorelin, and Hexarelin, have been researched for their potential in this area. Studies have suggested that these peptides may exert antifibrotic action, and lend support to tissue repair processes. One such peptide, BPC157, is widely considered to exhibit tissue healing characteristics, especially in its potential to promote tendon regeneration. Tendons are considered to be slow menders, but studies have suggested that BPC157 may speed up the process. Other peptides, like TB-500 and KPV, have been suggested to exert antimicrobial action to help ensure sterile wound healing.
Lean Muscle Structure
Sermorelin, CJC 1295, GHRP2, etc., are all hypothesized to impact the growth hormone axis, inducing an increase in bone density and muscle mass while dissolving fat cell collections. Ipamorelin has been posited to exhibit similar characteristics but with improved bone strengthening.
Disclaimer: The products mentioned are not intended for human or animal consumption. Research chemicals are intended solely for laboratory experimentation and/or in-vitro testing. Bodily introduction of any sort is strictly prohibited by law. All purchases are limited to licensed researchers and/or qualified professionals. All information shared in this article is for educational purposes only.