What is a Peptide?
The word peptide comes from the Greek word meaning “to digest.” Peptides are an important part of nature and biochemistry, and thousands of peptides occur naturally within the internal systems of organisms. With technological advances, new peptides are also being discovered and synthesized regularly in a laboratory settings.
The Formation Of Peptides
Peptides are formed both via natural processes within the organism and via synthetic processes inside the laboratory. Some peptides are manufactured organically, like ribosomal and nonribosomal peptides. In a laboratory, modern peptide synthesis processes may make a virtually infinite number of peptides using synthesis techniques like solid-phase or liquid-phase peptide synthesis. Solid-phase peptide synthesis is the standard process today, while liquid-phase peptide synthesis has some advantages. Vincent du Vigneaud synthesized the first Oxytocin, which is a polypeptide that was synthesized in 1953.
Classes
Peptides are divided into several classes. These classes vary based on how the peptides are produced. For example, the translation of mRNA produces ribosomal peptides. Ribosomal peptides appear to work as hormones and signaling molecules in organisms. These can include calcitonin peptides, vasoactive intestinal peptides, pancreatic peptides, and tachykinin peptide opioid peptides. Some organisms produce antibiotics like microcins, which are classified as ribosomal peptides. Ribosomal peptides mostly undergo the process of proteolysis, the breakdown of proteins into smaller peptides or amino acids to reach the mature form.
On the contrary, peptide-specific enzymes produce nonribosomal peptides. The ribosome does not produce them. Nonribosomal peptides are mainly cyclic rather than linear, although linear nonribosomal peptides may occur. Nonribosomal peptides may develop as extremely intricate cyclic structures. Nonribosomal peptides appear in plants, fungi, and single-celled organisms. Glutathione, suggested to be a significant part of antioxidant defense mechanisms in aerobic organisms, is the most common nonribosomal peptide.
Milk proteins may also form peptides in organisms. They may be produced by an enzymatic breakdown by digestive enzymes or by the proteinases formed by lactobacilli during the fermentation of milk. In addition, peptones are peptides from animal milk or meat that have been digested through proteolytic digestion. Peptones are used in the laboratory as nutrients for growing fungi and bacteria.
Moreover, fragments are commonly found as the products of enzymatic degradation in a laboratory with a control sample. However, peptide fragments can also occur naturally due to degradation by natural effects.
Terminologies to Know When Working with Peptides:
Amino Acids – Peptides consist of amino acids. An amino acid is any molecule that consists of both amine and carboxyl functional groups.
Cyclic Peptide – A peptide in which the amino acid sequence forms a ring structure instead of a straight chain. Examples of cyclic peptides are Melanotan-2 and Bremelanotide (PT-141).
Peptide Sequence – Is simply the order in which peptide bonds connect amino acid residues in the peptide.
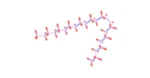
Peptide Bond – A covalent bond formed between two amino acids when a carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino-acid. This reaction is a condensation reaction, a reaction in which a molecule of water is released.
Peptide Mapping – Is a process that can be used to validate or discover the amino acid sequence of specific peptides or proteins.
Peptide Mimetics – Is a molecule that biologically mimics active ligands of hormones, enzyme substrates, cytokines, viruses, or other bio-molecules. Peptide mimetics can be a synthetically modified or natural peptide, or other molecules that perform the required function.
Peptide Fingerprint – It is a chromatographic pattern of the peptide. A peptide fingerprint is produced by partially hydrolyzing the peptide, which breaks up the peptide into fragments, and these are then undergone the 2-D mapping process.
Peptide Library – It consists of a large number of peptides that have a systematic combination of amino acids. Solid-phase peptide synthesis is the most frequent peptide synthesis technique that is used to prepare peptide libraries
Disclaimer: The products mentioned are not intended for human or animal consumption. Research chemicals are intended solely for laboratory experimentation and/or in-vitro testing. Bodily introduction of any sort is strictly prohibited by law. All purchases are limited to licensed researchers and/or qualified professionals. All information shared in this article is for educational purposes only.